MATHDES
Mathematical Design, Modelling and Simulations
 Mathematical Design, Modeling, and Simulations (MATHDES) group works on the design, analysis, implementation, and optimization of numerical schemes for mathematical models arising from real-life applications.
Mathematical Design, Modeling, and Simulations (MATHDES) group works on the design, analysis, implementation, and optimization of numerical schemes for mathematical models arising from real-life applications.
Principal Investigators:
Michael Barton and David Pardo
Our research spans areas of Deep Learning, Physics-Informed Neural Networks, Inverse Problems, Finite Elements, Computational Stochastics, High-performance scientific computing, Numerical Analysis, Geometric Modeling, Computer Aided Design, and Modeling of Manufacturing Processes. We work in close interaction with industrial partners and institutions to promote transfer of knowledge and obtain feedback from real-life applications.
Our research is funded by local, national, and European projects. Some examples of European projects include:
 (a) a FET-OPEN European project on Analysis, Design, and Manufacturing using Microstructures ADAM^2, which aims at revolutionizing the design-analysis-manufacturing pipeline, coordinated by Michael Barton;
(a) a FET-OPEN European project on Analysis, Design, and Manufacturing using Microstructures ADAM^2, which aims at revolutionizing the design-analysis-manufacturing pipeline, coordinated by Michael Barton;
 (b) a Marie Curie Staff Exchange Action MATHROCKS, intended to improve and exchange interdisciplinary knowledge on applied mathematics, high performance computing, and geophysics, coordinated by David Pardo;
(b) a Marie Curie Staff Exchange Action MATHROCKS, intended to improve and exchange interdisciplinary knowledge on applied mathematics, high performance computing, and geophysics, coordinated by David Pardo;
 (c) the European Doctoral Network IN-DEEP, intended to develop the next generation of physics-informed neural networks for solving Partial Differential Equations, coordinated by Judit Muñoz and David Pardo, and
(c) the European Doctoral Network IN-DEEP, intended to develop the next generation of physics-informed neural networks for solving Partial Differential Equations, coordinated by Judit Muñoz and David Pardo, and
(d) The Marie Curie Postdoctoral Fellow Projects:
(d.1) SWEATHEART, aimed to study the estimation of advanced cardiorespiratory parameters, such as the ventilatory thresholds, from wearable signals for improving the training plans of athletes. Coordinated by Tomás Teijeiro and Elisabetta de Giovanni.
(d.2) GEOLEARN, aimed to guide hydrogen storage technologies by inverting subsurface multiscale electromagnetic measurements in real time using energy-efficient artificial intelligence methods. Coordinated by Matteo Croci.
(d.3) GEODPG, aimed to design stabilized space-time adaptive techniques based on Discontinuous Petrov-Galerkin (DPG) methodology for the simulation of transient Partial Differential Equations (PDEs), with special emphasis on advection-dominated-diffusion and wave propagation problems. Coordinated by Judit Muñoz-Matute.
We collaborate with multiple prestigious institutions and industrial partners, including The University of Oxford (UK), The University of Cambridge (UK), The University of Texas at Austin (USA), Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (Switzerland), Stratasys LTD (Israel), INRIA (France), Simula Research Laboratory (Norway), Hutchinson S.A. (France), Seoul National University (South Korea), Technion - Israel Institute of Technology (Israel), Heriot-Watt University (UK), Harbin Institute of Technology (China), Macquaire University (Australia), Curtin University (Australia), Technical University of Wien (Austria), King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (Saudi Arabia), Software Competence Center Hagenberg (Austria), Pontifical Catholic University of Valparaíso (Chile), Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, National University of Colombia, Central University of Venezuela, University of Buenos Aires (Argentina), Barcelona Supercomputing Center (Spain), Polytechnic University of Catalonia (Spain), University of Barcelona (Spain), University Charles III of Madrid (Spain), Tecnalia (Spain), Trimek S.A. (Spain), and University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU).
A member of MATHDES is also co-founder of the international start-up Sensemodi, a company aimed at the development of wearable devices and decision support tools for preventive monitoring of patients with musculoskeletal and respiratory disorders.
This BCAM group has strong collaboration ties with the sister UPV/EHU Group MATHMODE.
In particular, we are currently involved in the following research projects:
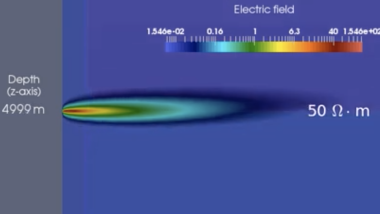
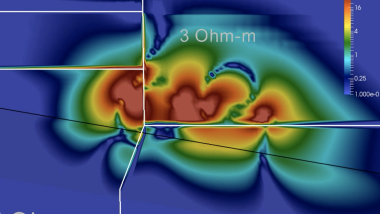
Deep Learning Algorithms for Inverse Problems: We study and develop Deep Learning methods to interpret (invert) in real-time elasto-acoustic and electromagnetic measurements. To achieve this objective, we design and implement proper Deep Neural Network architectures, loss functions, and error control algorithms enabling us to efficiently approximate physically meaningful inverse solutions.
Massive Finite Element Simulations: We develop a set of numerical Galerkin-based methods for producing massive synthetic datasets for training Deep Neural Networks. Some examples include variants of Isogeometric Analysis, Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms, Reduced Order Models, Proper Generalized Decompositions, and hp-Adaptivity.
Advanced Monte Carlo methods for high-performance uncertainty quantification. We develop state-of-the-art, scalable Monte Carlo methods for quantifying the uncertainty within computational models and estimate risks associated with incorrect predictions. The list of methods developed includes: multilevel Monte Carlo, quasi Monte Carlo, and importance sampling methods.
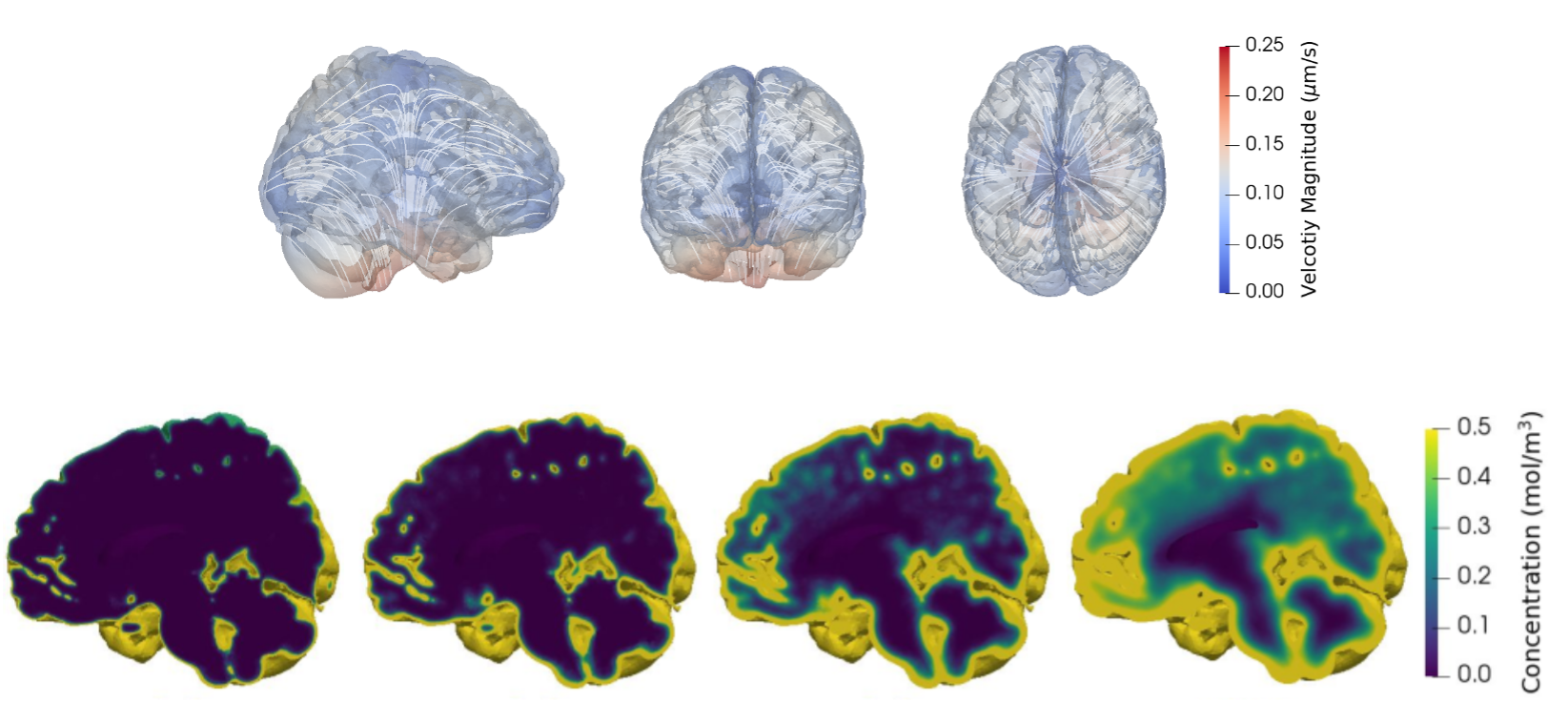
Biomedical computing and brain fluid simulation. We investigate the mechanisms behind brain solute clearance and neurodegenerative disease progression by simulating the brain fluid and solute dynamics and characterizing brain fluid velocities via Bayesian inference methods.
Geometric Modeling: We model manufacturing processes such as 5-axis Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) machining (see Fig. 1), hot-wire cutting, or hybrid (additive and subtractive) manufacturing.
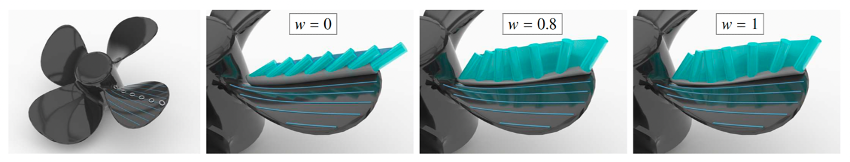
Fig. 1: Left: Optimized motions. On the propeller geometry (left), we show three optimized motions of the toroidal tool along the same contact path. The optimized tilt functions correspond to optimized accuracy (w = 0), balanced accuracy and tool-wear (w = 0.8), and minimized tool wear (w=1), respectively. All three paths are by construction physically feasible, i.e., globally collision-free.
Manufacturing Applications. In collaboration with the High-Performance Manufacturing Group (UPV/EHU), we design path-planning algorithms for multi-axis CNC machining. An example of a simulation of 5-axis flank milling with a custom-shaped tool is shown in Fig. 2. The tool and its motion are both unknowns in our optimization-based framework. Fig. 3 shows results of modeling and manufacturing of a lightweight blisk; its blade is filled by an interior microstructure and manufactured using hybrid manufacturing.

Fig. 2: Simulation of path-planning for 5-axis double-flank CNC machining of a spiral bevel gear using a custom-shaped milling tool, (left). The 3D-printed prototype of the designed tool is shown to the right.
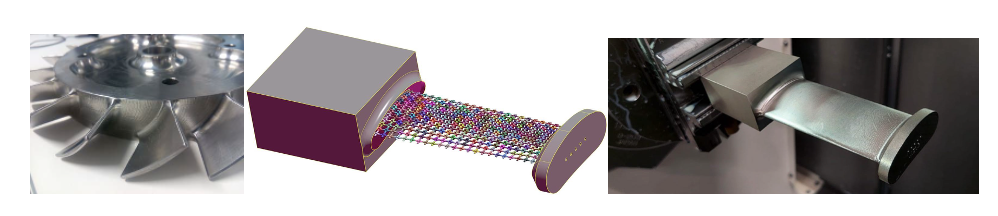
Fig. 3: Left: A blisk is a typical aeronautical workpiece. The whole blisk, including curved, free-form blades is usually solid which makes it a heavy component of an aero-engine. Middle: A microstructured alternative of one blade (before optimization) that sustains the prescribed stress limits, yet requires considerably less material (26% material reduction). Bottom: final microstructured blade manufactured using hybrid manufacturing (laser powder bed fusion + 5-axis CNC machining).
Continuous monitoring applications. This line of research focuses on the design of energy‑efficient algorithms for the continuous monitoring of sensor data in both health and industrial settings. Building on techniques such as predictive sensing, event‑based sampling, self‑supervised learning or hyperdimensional computing, we develop models that can run on low‑power embedded and wearable devices while preserving or even improving detection accuracy. In healthcare, these methods are used for long‑term monitoring of biosignals to characterize cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal and neurological conditions. In parallel, we transfer the same methodological principles to industrial applications, for example to large‑scale sensor networks for early detection and localization of hydrogen leaks, where minimizing latency, communication and energy consumption is critical for safety and reliability.
A Novel Multi-Resolution Heart Rate Variability Analysis for IoT-based Drowsiness Detection: Preserving Temporal Trends in Features Series
Hafidi, H.E.; De Giovanni, E.; Montanaro, T.; Sergi, I.; De Vittorio, M.; Patrono, L. (2025-07-30)
Heart rate variability (HRV) analysis provides valuable insights into autonomic nervous system regulation and serves as an effective indicator for drowsiness detection in transportation safety applications. This study presen...
Human-Centered and Context-Aware Smart ML-based IoT Framework for Online Fatigue Detection: a Real-World Study of Football Training
Mamen, A.; De Giovanni, E.; Montanaro, T.; Sergi, I.; Patrono, L. (2025-12-08)
Fatigue is one of the factors that most influences competitive athletes’ performance, leading to injuries and overtraining. To effectively monitor and predict fatigue levels during real-world training, it is necessary to int...
Variational Autoencoder-Based Alert System for Onshore Wind Turbine: Application to a Real Case Study
Zamora-Sánchez, D.; Fernandez-Navamuel, A.; Pardo, D.; Magalhães, F.; Pereira, S. (2025-10-01)
Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) of wind turbines is still far from a practical and effective implementation. One of the main limitations is the access to long-term experimental data from operative systems, as well as the ...
A Copula-based variational autoencoder for uncertainty quantification in inverse problems: application to damage identification in an offshore wind turbine
Fernandez-Navamuel, A.; Diaz Viera, Martin A.; Croci, M. (2026-01-01)
Structural health monitoring of floating offshore wind Turbines (FOWTs) is critical for ensuring operational safety and efficiency. However, identifying damage in components like mooring systems from limited sensor data pose...
Solving Partial Differential Equations using Artificial Neural Networks
Damage identification in bridges combining deep learning and computational mechanic
CL file
Datasets (Zenodo) for the paper "Manufacturing of screw rotors via 5-axis double-flank CNC machining"
Authors: Michael Barton, Michal Bizzarri
License: Zenodo
CL file
Datasets (Zenodo) for the paper "Geometry and tool motion planning for curvature adapted CNC machining"
Authors: Michael Barton, Michal Bizzarri, Oleksii Sliusarenko, Florian Rist, Helmut Pottmann
License: Zenodo